Introduction:
Department of Medical Education (DME) named Dental Education and Research Department (DERD) was established in 2017 for strengthening undergraduate and postgraduate training for AIDM. Department of Medical Education is responsible for introducing new initiatives and the philosophical underpinnings for improvement of educational programs and developing leaders to accomplish learning outcomes.
The focus is on areas of educational pedagogy and university curriculum, evaluating future directions for dental education by examining the status of oral health in our country and the ramifications for dental education in both the short and the long-term.
The department participates in key educational committees which are Academic Council,
Curriculum, Research, Journal, Disciplinary, Examination committees and Quality Enhancement activities
Mission statement:
To support excellence in faculty and students training by providing opportunities and innovation, introducing new teaching, assessment, evaluation methods and educational activities. Facilitates in scientific research and scholarly effort in the oral health and health professions education, ensuring appropriate and compassionate oral health care for individuals and responsiveness to community needs.
Scope:
DME is advisory to the President, Deans & Principal and committed to:
Provide faculty development workshops and certificate course in health professions education (CHPE) for capacity building of the faculty.
Guide the faculty regarding the structure of the curriculum including sequencing of content and most appropriate teaching, learning and assessment methods to meet undergraduate and post graduate programs learning outcomes.
Facilitate in development of educational, research innovations, continuous dental education activities and support systems to promote evidence based education.
Full-time Faculty:
Dr. Shaur Sarfaraz: Director & Assistant Professor
Dr.Alizay jaffery: Lecturer
Dr.Rubab Hashim: Lecturer
Other Faculty:
Prof. Ambreen Afzal Ehsan: Dean Academics
Members from Students Section:
Ms. Mani Badha: Director Admissions
Ms. Sanam Qamar: Assistant Director Admissions & Coordinator Student Section
Apply now for certification in health professions Education CHPE:
Anatomy is the science of Structure or form of the body. It can be subdivided into Gross/Macroscopic and Microscopic Anatomy. Gross anatomy is the study of structures large enough to be seen with the naked eye while Microscopic Anatomy including histology and embryology, is microscope based.
It is very important for a doctor to have a good grasp of anatomy in order to understand body systems and functions
Biochemistry is the science concerned with the chemical basis of life.
Students who acquire a sound knowledge of biochemistry will be in a strong position to deal with central concerns of the health. The knowledge of Biochemistry is essential to understand specific dental problems such as caries
and plaque formation. The students must be equipped as far as possible for a lifetime in an era of rapid progress and change as research and diagnostic techniques are becoming more and more biochemically orientated.
 Oral biology is a branch of dentistry encompassing the disciplines of molecular biology, oral anatomy, genetics, immunology, craniofacial development, pharmacology, physiology and cancer biology. Because of the unique combination of tissues and functions of mouth with craniofacial complex, the field of oral biology blends fundamental scientific disciplines in unique and fascinating way to meet the challenges of developing new and highly effective way to manage, cure or prevent diseases and developmental defects
Oral biology is a branch of dentistry encompassing the disciplines of molecular biology, oral anatomy, genetics, immunology, craniofacial development, pharmacology, physiology and cancer biology. Because of the unique combination of tissues and functions of mouth with craniofacial complex, the field of oral biology blends fundamental scientific disciplines in unique and fascinating way to meet the challenges of developing new and highly effective way to manage, cure or prevent diseases and developmental defects
The Department of Oral Medicine/ Oral Diagnosis at AIDM focuses on the oral healthcare, diagnosis, and management, of medically complex patients, encompassing non-dental pathologies within the oral cavity and orofacial region. As a primarily non-surgical specialty, procedures are generally limited to diagnostic biopsies, minor excisions, therapeutic injections, and other minimal invasive interventions. Medical management often involves the utilization of topical and systemic medications.
In this department, outdoor patients undergo comprehensive screening and examination to establish a primary diagnosis. Cases falling within the Oral Medicine specialty’s purview, including medical emergencies, orofacial pain, neuralgia, oral lesions, ulcerative conditions, temporomandibular joint disorders, and oral infectious lesions, are managed internally. Conversely, patients requiring specialized care are counselled and referred to relevant departments.
Accurate record-keeping is maintained through both manual and digital registration using Health Management Information System (HMIS) software. Collaboration with the radiology department enables access to various diagnostic radiographs, such as orthopantomograms, bitewing, and periapical radiographs, facilitating precise diagnosis.
Furthermore, the Oral Medicine department is committed to providing clinical training to Bachelor of Dental Surgery (BDS) students and house officers through regular case demonstrations and small group discussions. Emphasis is placed on evidence-based teaching methodologies to ensure optimal educational outcomes.
This department plays a vital role in integrating academic and clinical expertise to deliver comprehensive patient care.
Physiology is the study of functions of living matter. It is the study of life, specifically how cells, tissues and organisms function. Physiology is important because it is the foundation upon which we build our knowledge of what ‘life’ is, how to treat diseases, and how to cope with stresses imposed upon our bodies by different environments.
Pathology involves study of diseases while microbiology is study of characteristics of microbes that may be the cause of these diseases. This medical specialty will help student relate various diseases to their cause, mechanism and clinical features, thereby aid in diagnosis of diseases.Moreover, students will study the changes that will occur in a diseased organ, both macroscopically and microscopically
The BDS Pharmacology course deals in the area of drug and related compounds. It includes the details of medicines such as their origin, function, uses and adverse effects. It also emphasizes the drug with drug and drug with food interactions.
The curriculum comprises of the details of all the main drugs being used with the focus on future practical life as a dentist working in the community.
Community and preventive dentistry, a pre-clinical subject is taught to the 2nd year BDS students.
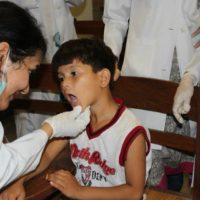
Our society despite major advancements in oral health research and healthcare now a days, faces major challenges in the form of widespread prevalence of oral health conditions. This is mostly due to lack of oral health awareness amongst the population especially those with low socio-economic status. The goal of this dental specialty is to train the aspiring dentists to think of oral health problems and of their solutions with respect to the community leading to an increase in oral health awareness in our society thereby preventing the occurrence of such problems.
Keeping the goal of establishing oral health preventive practices and as a part of teaching strategy, the students are made to visit different schools, communities and public places where they provide free dental check-up to the people from different age groups and demonstrate preventive procedures. Creating health awareness and educating the masses is carried out to control the curative burden on a limited health budget that our countrymen can avail.
The Science of Dental Materials includes the study of dental biomaterials that are used to restore decayed, damaged, fractured or missing teeth. It deals with the study of different types of materials including metals, porcelain, glass-like ceramics, waxes and polymers to name a few. There is a detailed account of manufacturing, chemical and mechanical characteristics and biocompatibility of the specially designed materials used in dentistry that enables proper usage of these materials in the dental laboratory and in clinical practice.
 Oral pathology is the speciality of dentistry and pathology which deals with the nature, identification and management of disease affecting the oral and maxillofacial regions. It is a science that investigates the cause, processes and effects of these diseases. The practice of oral pathology includes research, diagnosis of disease using clinical, radiographic, microscopic, biochemical or other examinations and management of patients
Oral pathology is the speciality of dentistry and pathology which deals with the nature, identification and management of disease affecting the oral and maxillofacial regions. It is a science that investigates the cause, processes and effects of these diseases. The practice of oral pathology includes research, diagnosis of disease using clinical, radiographic, microscopic, biochemical or other examinations and management of patients
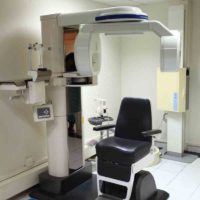
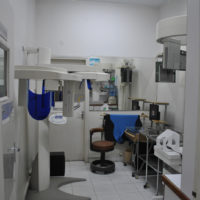
The radiology department is equipped with the latest technology in the world i.e. Digital radiography. This digital imaging system uses non-film solid state detectors to capture radiographic exposure. These digital radiographic images are then displayed across various departments on high definition monitors. Minimal radiation exposure and optimization of digital radiographs are the major advantages of digital radiography.
Cone Beam Computed Tomography (CBCT) at AIDM
The Altamash Institute of Dental Medicine boasts of the latest and state of the art imaging technologies in the current world of dentistry. Cone beam computed tomography (or CBCT) is a medical imaging technique consisting of X-ray computed tomography where the X-rays are divergent, forming a cone.
AIDM has been a premier pioneer facility for Dental Implants and education as well. CBCT has become increasingly important in treatment planning and diagnosis in implant dentistry as well. CBCT scanners are now finding many other uses in dentistry, such as in the fields of Endodontics and Orthodontics.
With the use of CBCT at AIDM, visualization of a Dental Implant procedure or Orthodontic treatment has become even more convenient.
CBCT use in implantology
A dental cone beam scan offers invaluable information when it comes to the assessment and planning of surgical implants. The AAOMR also suggested cone-beam CT as the preferred method for presurgical assessment of dental implant sites.
CBCT use in orthodontics
As a 3D rendition, CBCT offers an undistorted view of the dentition that can be used to accurately visualize both erupted and non-erupted teeth, tooth root orientation and anomalous structures that conventional 2D radiography cannot.
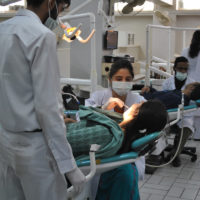
The Department of General Surgery provides comprehensive surgical consultation and care in many subspecialties. Students are trained in consultation, history taking, treatment planning, preoperative and post-operative management by doctors skilled in their discipline.
The General Medicine Department is run by a dedicated and highly motivated team. Students are trained in consultation, history-taking, general physical examination, detailed systemic examination, treatment planning and disease management by doctors skilled in their discipline.
Orthodontics is a branch of specialized dentistry that deals with the prevention and correction of dental and facial anomalies. The main aim of orthodontic treatment revolves around the safe movement of teeth into proper alignment, guiding of facial development while ensuring healthy growth in the jaw.
Services provided by the Department of Orthodontics at Altamash Institute of Dental Medicine to the public begin with comprehensive clinical examination, diagnosis and effective treatment planning and counseling for patients. Orthodontic treatment is available for the early childhood, adolescent and adult phase with the use of both traditional and modern day appliances. This includes collaborative team efforts with oral maxillofacial surgeons for severe jaw discrepancy cases. Every effort conducted is in the best interest of the patient, providing results that show dramatic aesthetic and functional improvements. Patients are also offered state of the art fixed and removal functional appliances for comprehensive treatment. With feasible rates kept for the general public, the Department generates great patient turn over on a regular basis.
Prosthodontics is a specialized field of dentistry that deals with the replacement of missing teeth and associated structures. We pertain to the diagnosis, treatment planning, rehabilitation, and maintenance of the oral function, comfort, appearance and health of patients with clinical conditions associated with missing or deficient teeth; providing fixed and removable partial dentures for partially edentulous patients and removable complete dentures for completely edentulous patients and splints for TMDs. Also deal with the restoration of missing maxillofacial structures.
Operative Dentistry is the branch of dentistry which deals with the identification, prevention and treatment of the teeth which have undergone the destruction of the tooth structure either due to dental decay, infection, dental decay or trauma. The process of all these procedures involves patient educating regarding the dental problems, doing the fillings of the decayed teeth and doing the root canal treatment of infected teeth. Root canal treatment involves removal of the infected nerves from the tooth to relieve the pain and to prevent the progress of infection which may ultimately lead to tooth loss. Dealing with kids to teach them their basic dental needs up to treating their dental problems is also the part of operative dentistry which may extend up to dealing them under General anesthesia if required.
Periodontology is an integral part of Altamash Institute of Dental Medicine, which deals with the diagnosis, treatment, & prevention of the gum diseases. Procedures that are carried out in the Department include professional cleaning, polishing, deep scaling (curettage), corrective gum surgeries, gingivectomy etc. The Department of Periodontology is committed to expanding its innovative educational program, transmitting scientific knowledge through study and discovery and enhancing the superior skills of our predoctoral and graduate students, faculty and staff.
 Oral surgery is a branch of dentistry that deals with the diagnosis and treatment of oral conditions requiring surgical intervention. Here in the oral surgery department at the Altamash institute of dental medicine we perform an array of procedures including removal of impacted teeth, difficult tooth extractions(surgical and non-surgical), removal of wisdom teeth, extraction of rotten or broken teeth, and the removal of carious or sound primary teeth that did not fall out naturally, extractions on medically compromised patients, removal of teeth in order to align teeth properly with the help of braces and preprosthetic surgery to provide better anatomy for the placement of implants, dentures, or other dental prostheses. We also diagnose and treat facial pain disorders, including those caused by temporomandibular joint (TMJ) problems.
Oral surgery is a branch of dentistry that deals with the diagnosis and treatment of oral conditions requiring surgical intervention. Here in the oral surgery department at the Altamash institute of dental medicine we perform an array of procedures including removal of impacted teeth, difficult tooth extractions(surgical and non-surgical), removal of wisdom teeth, extraction of rotten or broken teeth, and the removal of carious or sound primary teeth that did not fall out naturally, extractions on medically compromised patients, removal of teeth in order to align teeth properly with the help of braces and preprosthetic surgery to provide better anatomy for the placement of implants, dentures, or other dental prostheses. We also diagnose and treat facial pain disorders, including those caused by temporomandibular joint (TMJ) problems.
We also diagnose and treat patients with benign cysts, lesions and infections of the oral cavity including incision and drainage. We perform frenectomy (surgical removal of frenulum), gingivectomy (removal of ginigival overgrowths) and biopsy(removal of diseased oral tissue for diagnosis). We also facilitate patients with dental trauma. We are also equipped with an OPG machine that enables us to carryout comprehensive diagnostics prior to any surgical procedure.
Research is an integral part of the mission at AIDM. Through creativity, dedication, hard work and commitment, our investigators shape the future of dental medicine and dental education.
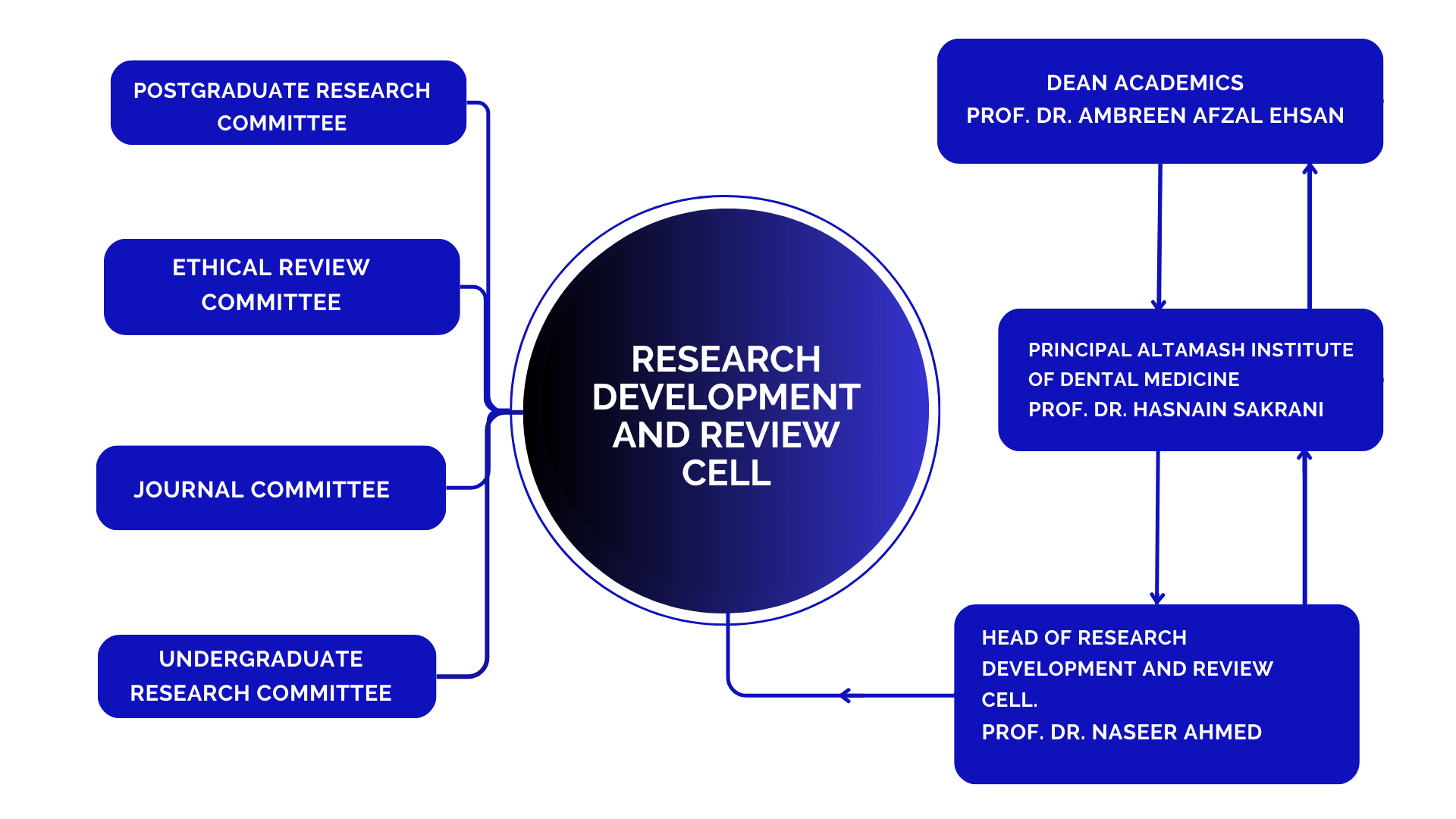
RESEARCH DEVELOPMENT AND REVIEW CELL (RDRC) OF ALTAMASH INSTITUTE OF DENTAL MEDICINE
Organogram
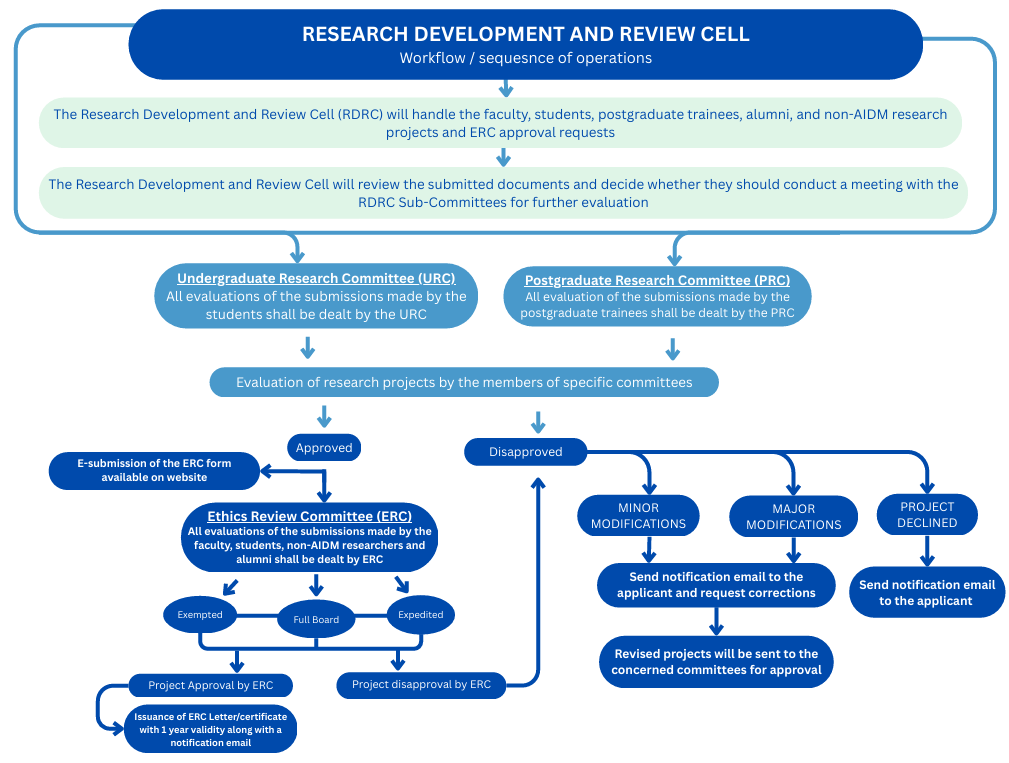
RESEARCH DEVELOPMENT AND REVIEW CELL (RDRC)
Workflow/Sequence of Operation
Rational of RDRC
The Research development and Review Cell (RDRC) is to enhance oral health by transferring basic and applied research knowledge and new technical advances into patient-oriented research Project. The purpose of the department is to give dental students a chance to experience both basic and clinical research from a hands-on perspective by participation in an ongoing research investigation that to promote research culture in students and faculty. Enhance research capabilities of AIDM. Produce potential researchers and add scientific knowledge in national and international databases.
The research plan outlines the goals, objectives, and strategies to foster a culture of research and innovation within AIDM. The primary aim is to encourage support and facilitate high-quality research among undergraduate and postgraduate students, faculty members, and researchers
I. Vision
To be recognized as a leading center for dental research promoting innovation, and advancing oral healthcare
II. Mission
To create an environment that promotes research, encourages critical thinking, and develops evidence-based approaches to oral health.
III. Objectives
To promote research awareness and interest among undergraduate BDS, house surgeons, and Postgraduate Students.
To support and facilitate faculty members in conducting research and publishing in reputable journals
To establish interdisciplinary collaboration within the institution and with other dental and medical institutions.
To promote ethical research practices and adhere to national and international research guidelines.
Extending Research Opportunities
In addition to building oral health research capacity by training more and better researchers and policymakers should also explore creative strategies to extend traditional avenues for acquiring clinical knowledge and to make use of untapped faculty resources. Such strategies will also help college to respond to patient and purchaser pressure for more and quicker information about the effectiveness of different clinical strategies.
Focus of Research and Research Training
To build clinical and basic science research opportunities for undergraduate to enrich their education in the research capacity and resources as well as foster relationships with other researchers, that they can take advantage of the statistical, data base, communications, measurement, and other research techniques and protocols that are emerging from the growing field of outcomes research.
Expanding Research Capacity and Accomplishments
The student conduct research within the dental college and also collaborate with other colleges. The students who are involved in research have opportunities to author manuscripts, present their results at national and international conferences’, and successfully compete for awards and grants inside and outside of the dental college and also to published in AJDMS journal.
Benefits of Research Development and Review Cell
- Support a research program that includes clinical research, evaluation and dissemination of new scientific and clinical findings, and research on outcomes, health services, and behavior related to oral health
- Enhance its research program, when feasible, to the basic sciences and to the transformation of new scientific knowledge into clinically useful applications.
- Look forward to all faculty to be critically knowledgeable about scientific advances in oral health and to stay current in their teaching and practice and encourage all faculty to participate in research.
- Continue to evaluate and improve its extramural training and development programs.
- Focus more resources on those extramural programs with greater demonstrated productivity in strengthening the oral health research capacity of dental schools and faculties
- Preserve some funding for short-term training programs intended primarily to increase research understanding and appreciation among clinical teaching faculty and future practitioners.
Structure of the Research Development and Review Cell
Altamash Institute of Dental Medicine
The AIDM-RDRC is composed of a minimum of the following members:
- Chairperson
- Deputy Chair
- Senior Medical Academics/Senior Health Professionals
- Continue to evaluate and improve its extramural training and development programs.
a) Medical (at least one)
b) Dental (at least one)
c) Health (at least one) - Statistician (at least one)
- Non Institutional Members (at least one)
- Social/Behavioral Scientist (meaning not in medical, dental or any allied health sciences) (at least one)
- Female Member (at least one if not represented in any of the above group)
- Member Secretary (at least one)
Specific Duties and Functions
Chairperson:
- Recommends committee members
- Recommends policy amendments and changes
- Supervises meetings
- Represents AIDM-RDRC in national and international ethics forum
- Coordinates with stakeholders outside AIDM
- Classify the review (full board, expedited or exempted) for initial protocol submissions
- Oversees the operations of the AIDM-RDRC and all subcommittees
- Supervises the management of the AIDM-RDRC Office
- Acts on suggestions, complaints, and queries from stakeholders
- Ensures AIDM-RDRC compliance with international, national and institutional policies governing human subject research
- Ensures budget adequacy for AIDM-RDRC operations and activities
Deputy Chair:
- Chairs meetings when the Chair is absent or unable to perform the duties of the Chair.
- Assume the responsibilities of the Chair in his absence.
Member Secretary:
- Oversee preparation and accuracy of the agenda of the meeting.
- Supervise the preparation of the minutes of the meeting and approved the minutes of the meeting
- Familiarize him/herself with the international and national guidelines on research ethics
- Participate actively in the Full Board Review meetings and other AIDM-RDRC meetings.
- It is expected that a member secretary will have at least 50% attendance during the period of appointment
- Perform other AIDM-RDRC related tasks that may be assigned to him/her by the
Chairperson
Secretary
- Prepares and issues the schedule of every AIDM-RDRC meetings
- Prepares the meeting agenda and ensure all necessary documents are attached to the agenda
- Makes prior review of the applications to ensure their completeness
- Distributes the agenda and papers
- Sends out invitation to Principal Investigator(s) notifying the date to attend the meeting atleast five (5) working days in advance
- Prepares the venue of the meetings
- Takes minutes of the meeting
- Is not eligible for voting or giving opinion in the meeting
- Destroys the copies of the proposals which have been reviewed immediately after the meeting leaving the master copy for archiving
- Ensures the minute of the meeting which is tabled is checked by the chairperson prior the next meeting.
- Notifies applicants on decisions taken at the meeting and taking other follow-up action as necessary
- Archives the meeting records
AIDM-RDRC Members
- Make a timely and thorough review and decision regarding protocols given to them for evaluation
- Familiarize themselves with the SOPs and the international and national guidelines on research ethics
- Participate actively in meetings of AIDM-RDRC. In the event of multiple absences without valid reason, the member can be recommended to be replaced.
- Participate in decision making
- Participate in the review of the progress reports, final reports and other amendments presented during the meeting
- Maintain confidentiality of the documents and meeting
- Declare any conflict of interest in general and for specific protocols for review
- Participate in required training with proof of attendances
- Submit an updated and signed CV at the start of each term of appointment
- Refer to the Chair for any suggestions, complaints or grievances of research participants, PIs, and/or sponsors.
- Do other AIDM-RDRC related duties that maybe requested of him/her by the Chair when necessary
ETHICAL REVIEW COMMITTEE
Principles
Principles that govern research with human subjects:
- Human subject should provide voluntary consent and know the risks of participation.
- The experimental results should be for the greater good of society.
- Experiment should be based on previous animal experimentation.
- Experiment should avoid unnecessary physical/mental suffering.
- No experiments should be conducted if it is believed to cause death/disability.
- Benefits must always outweigh the risks.
- Adequate facilities should be used to protect subjects.
- Experiment should be conducted only by qualified scientists.
- Subject should always be at liberty to stop at any time.
- Scientist in charge must be prepared to terminate the experiment when injury, disability or death is likely to occur.
Basic Principles:
The fundamental principle is respect for the individual, their right to self-determination and the right to make informed decisions regarding participation in research, both initially and during the course of the research.
- The investigator’s duty is solely to the patient or volunteer, and while there is always a need for research, the subject’s welfare must always take precedence over the interests of science and society, and ethical considerations must always take precedence over laws and regulations.
- The recognition of the increased vulnerability of individuals and groups calls for special vigilance. It is recognized that when the research participant is incompetent, physically or mentally incapable of giving consent, or is a minor, then allowance should be considered for surrogate consent by an individual acting in the subject’s best interest, although their
consent should still be obtained if at all possible.
Operational Principles:
- Research should be based on a thorough knowledge of the scientific background, a careful assessment of risks and benefits, have a reasonable likelihood of benefit to the population studied and be conducted by suitably trained investigators using approved protocols, subject to independent ethical review and oversight by a properly convened committee.
- The protocol should address the ethical issues.
- Studies should be discontinued if the available information indicates that the original considerations are no longer satisfied.
- Information regarding the study should be publicly available.
- Ethical publications extend to publication of the results and consideration of any potential conflict of interest.
- Experimental investigations should always be compared against the best methods, but under certain circumstances a placebo or no treatment group may be utilized.
Full Board Review:

Full Board
If the project involves more than minimal risk to participants, project requires a Full Board review. Protocols involving any of the following will
also require Full Board review:
1. Minor subjects (children 17 years of age or younger)
2. Special populations (prisoners, pregnant women, individuals with disabilities)
3. The use of video- or audiotape to record subjects
4. Asking questions that may be highly embarrassing or compromising (e.g., sexual behavior, sexual orientation, alcohol consumption, illegal
drug use, medical conditions, violations of the law, personal finances, problems in the workplace, etc.)
5. Inflicting physical pain upon, attaching electrodes to, or injecting any substance into subjects
6. Creating high levels of stress, fear, discomfort, or tension
7. Threatening subjects in any way
8. Causing subjects to violate laws or official university regulations
9. Providing some subjects with benefits denied to others (this includes payments or rewards for participation, e.g., offering extra credit to
participants, etc.)
10. Causing physical or mental exhaustion or engaging subjects in intense exercise
11. Placing individuals in confining physical settings or attaching other devices
12. Exposing subjects to extreme conditions (e.g., bright lights, loud noise, intense pressure, strong odors, complete darkness, extreme heat or
cold, sudden movement, etc.)
13. Leaving subjects alone for periods of time longer than 20 minutes
14. Taking hair samples or nail clippings from subjects
15. Taking human tissue samples, drawing blood, or sampling any other bodily fluid
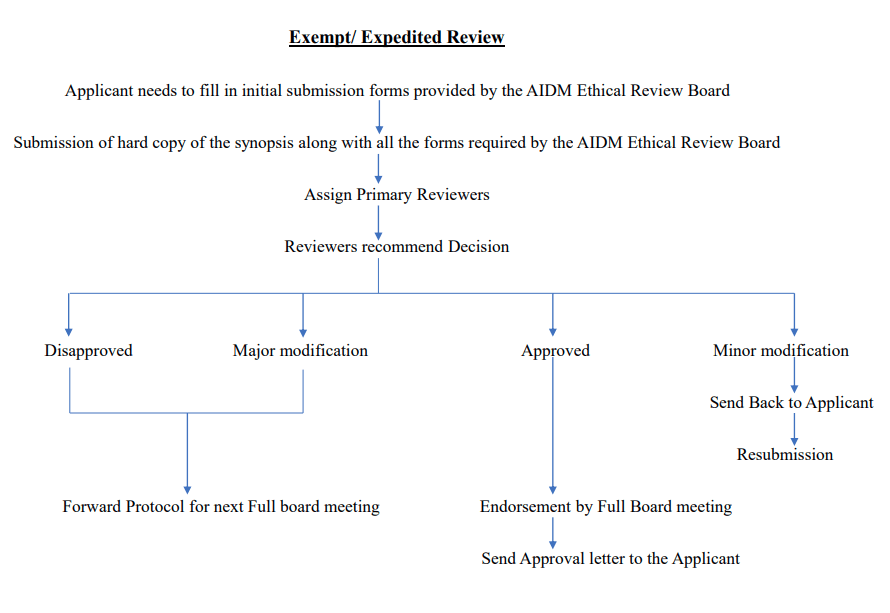
Exempt
Research that is classified as Exempt will not require any further review after the initial approval and only needs to be reviewed by the chair of the IRB.
Categories of Research that qualify as Exempt:
1. Research conducted in established or commonly accepted educational settings, involving normal educational practices, such as
(i) research on regular and special education strategies, or
(ii) research on the effectiveness of or the comparison among instructional techniques, curricula, or classroom management methods.
2. Research involving the use of educational tests (cognitive, diagnostic, aptitude, achievement), survey procedures [if minors are involved, Full Board review is
required], interview procedures [if minors are involved, Full Board review is required], or observation of public behavior UNLESS
(i) Information obtained is recorded in such a manner that human subjects can be identified, directly or through identifiers linked to the subjects, and
(ii) Any disclosure of the human subjects’ responses outside the research could reasonably place the subjects at risk of criminal or civil liability or be damaging to the subjects’ financial standing, employability, or reputation.
3. Research involving the use of educational tests (cognitive, diagnostic, aptitude, achievement), survey procedures, interview procedures, or observation of public
behavior that is NOT already Exempt under #2 if:
(i) The human subjects are elected or appointed public officials or candidates for public office, or
(ii) Federal statute(s) require(s) without exception that confidentiality of the personally identifiable information will be maintained throughout the research and thereafter.
4. Research involving the collection or study of existing data, documents, records, or pathological or diagnostic specimens, if these sources are publicly available or if
the information is recorded by the investigator in such a manner that subjects cannot be identified directly or through identifiers linked to the subjects.
5. Research and demonstration projects which are conducted by or subject to the approval of [Federal] Department or Agency heads and which are designed to study,
evaluate, or otherwise examine:
(i) Public benefit or service programs,
(ii) procedures for obtaining benefits or services under these programs,
(iii) possible changes in or alternatives to those programs or procedures, or
(iv) payment for benefits or services under those programs.
6. Taste and food quality evaluation and consumer acceptance studies,
(i) If wholesome foods without additives are consumed or
(ii) if a food is consumed that contains a food ingredient at or below the level and for a use found to be safe, or agricultural chemical or environmental contaminant at or below the level found to be safe, by the Food and Drug Administration or approved by the Environmental Protection Agency or the Food Safety and Inspection Service of the U.S. Department of Agriculture.
Expedited
Research that is classified as Expedited only needs to be reviewed by the chair or by a qualified member of the IRB that has been designated by
the chair. It is, however, subject to annual review.
A research project is appropriate for Expedited review if it involves only minimal risk, but is not classified as Exempt. Minimal risk is defined as risk that is not greater than what one encounters in ordinary daily life or during the performance of routine physical or psychological examinations or tests.
AIDM ERC Form
ERC AIDM Synopsis Template
THESIS GUIDELINES
Publication Consent Form
Consent Form
Data Collection Permission Form